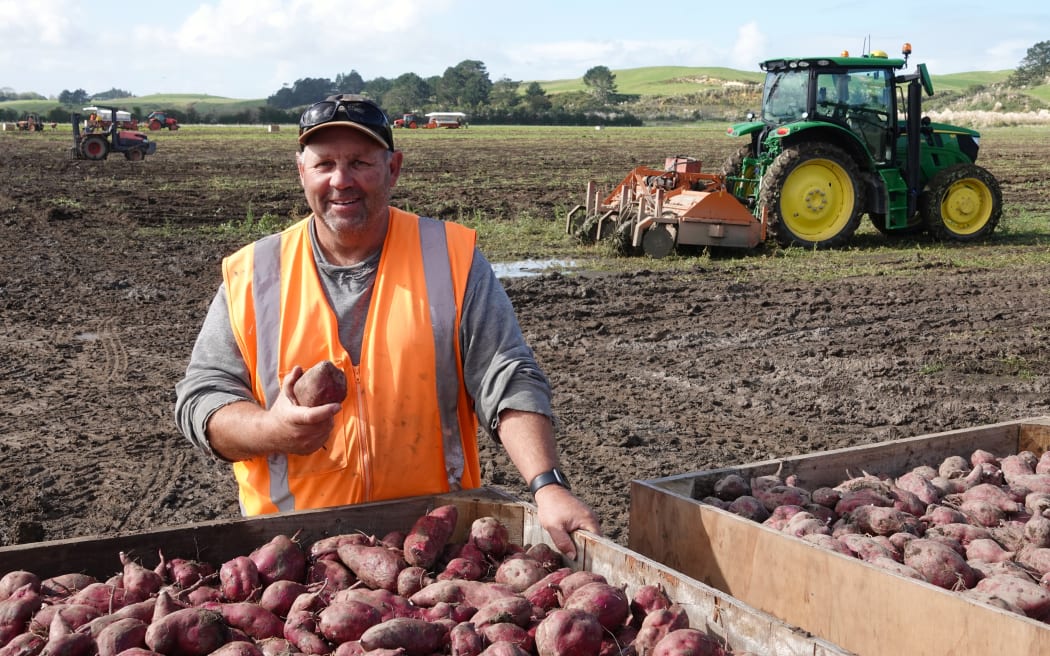
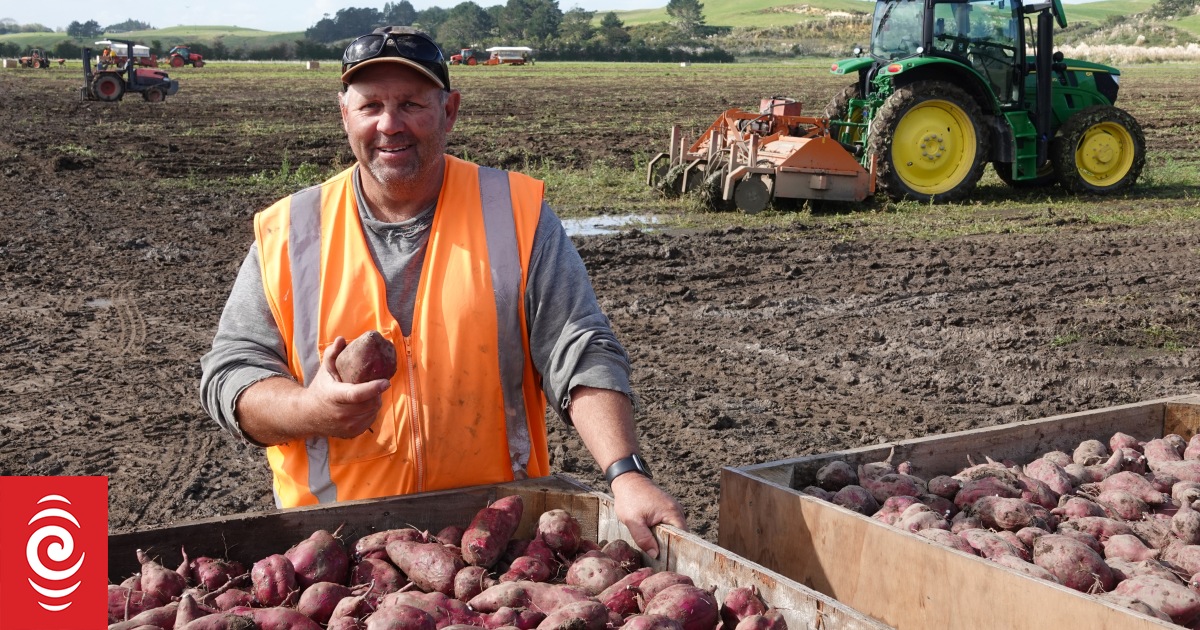
Dargaville kumara grower Doug Nilsson checks the seed kumara that will form the basis of next year’s crop.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
One year ago, the future for New Zealand’s favourite root vegetable looked bleak.
After a dismal spring and summer, Cyclone Gabrielle turned large swathes of the Kaipara – where virtually all New Zealand’s kumara are grown – into a vast inland sea, causing the harvest-ready crop to rot in the ground.
Grower Doug Nilsson, of Dunsmore Gardens on the outskirts of Dargaville, lost 99 percent of his crop, managing to salvage and sell fewer than 30 bins of kumara.
But the 2024 season has been very different.
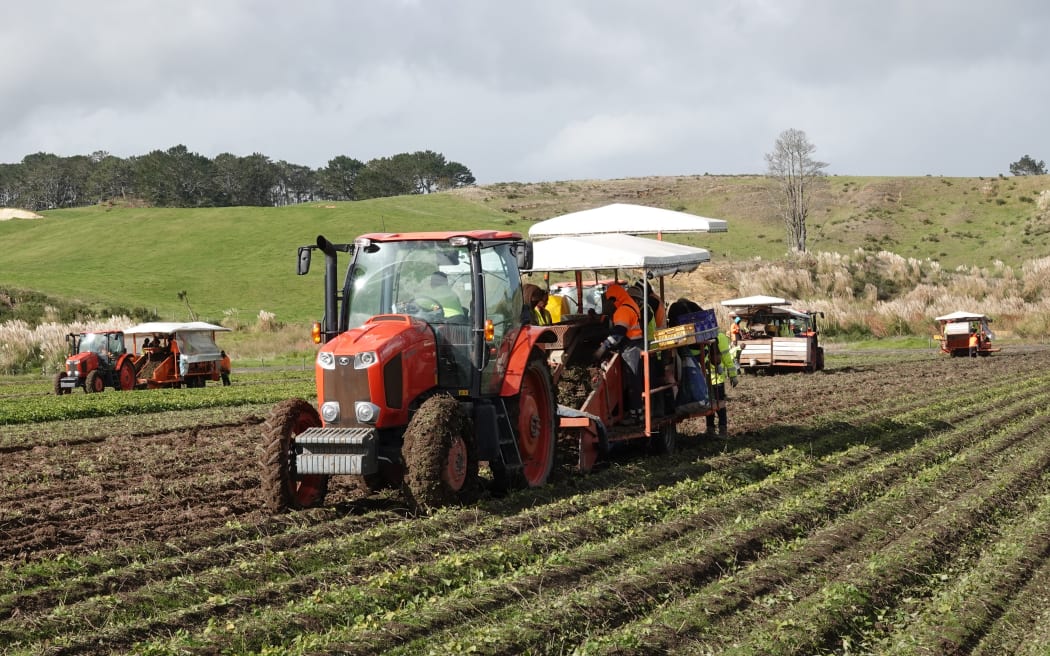

Harvesting crews gather the last of Doug Nilsson’s 2024 crop at his farm on the outskirts of Dargaville.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
Last week, Nilsson filled the last of 2900 bins, each containing about 750kg of kumara – 100 times more than the year before.
While the yield was not his biggest ever, harvest conditions were the best he had experienced in 20 years.

Dargaville kumara grower Doug Nilsson reflects on a roller-coaster couple of years.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
“Last season was a shocker. Cyclone Gabrielle was just the last straw in a really bad growing year. It came off the back of a record wet winter, a really wet difficult planting season, in which most growers, ourselves included, were lucky to get 60 percent of their normal crop planted. And then a wet summer, Cyclone Hale and Cyclone Gabrielle,” Nilsson said.
It was not just his crop that was affected – housing for his workers was also submerged.
“The accommodation had about a metre of water through it. It took until Christmastime to get the workers back into here. That’s been the one bugbear, the time it takes before you can do anything, waiting for insurance. We still haven’t been fully paid out.”
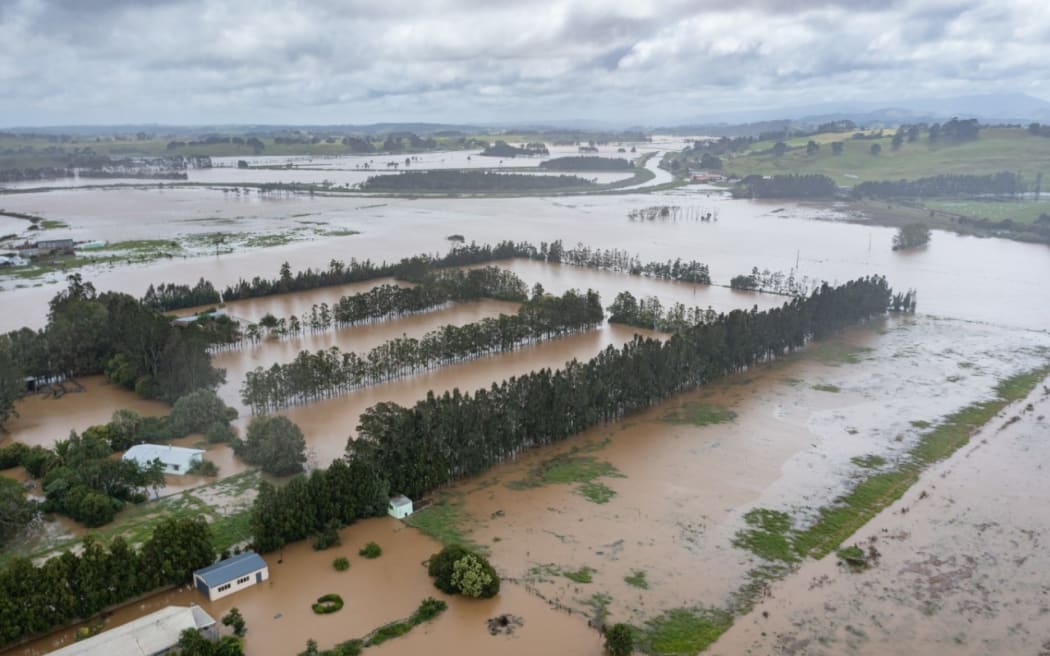

Kaipara’s Kaihu River north of Dargaville in flood during Cyclone Gabrielle in 2023.
Photo: Kaipara District Council / Supplied
The loss rippled across Northern Wairoa, where kumara growing vied with dairy for the title of the area’s biggest earner.
“It affects everybody because we’re at the start of the chain. If we’ve got no kumaras to harvest, there’s no work – that corresponds to less money spent in town. It also affects our trucking firms that carry the kumaras – nothing to cart. Even our local bin builder, he had a terrible year last year because no one needed bins. It’s a snowball effect.”
The 2024 season, however, had been the “complete opposite”.
“The yields are a bit lighter than average but we’ve had tremendously good weather and good digging conditions for harvest. The shed’s full of nice kumara, really good quality this year. It’s probably the best harvest I’ve had in 20 years.”

Harvesting crews gather the last of Doug Nilsson’s 2024 crop at his farm on the outskirts of Dargaville.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
Nilsson said he had also been lucky with reliable staff this year, a 50-50 mix of locals from Kaipara, Kaikohe and Whangārei, and overseas workers employed through the RSE (recognised seasonal employer) scheme.
Many of those sorting the kumara pulled from the clay soil were, like Mansen Makito, from Vanuatu.
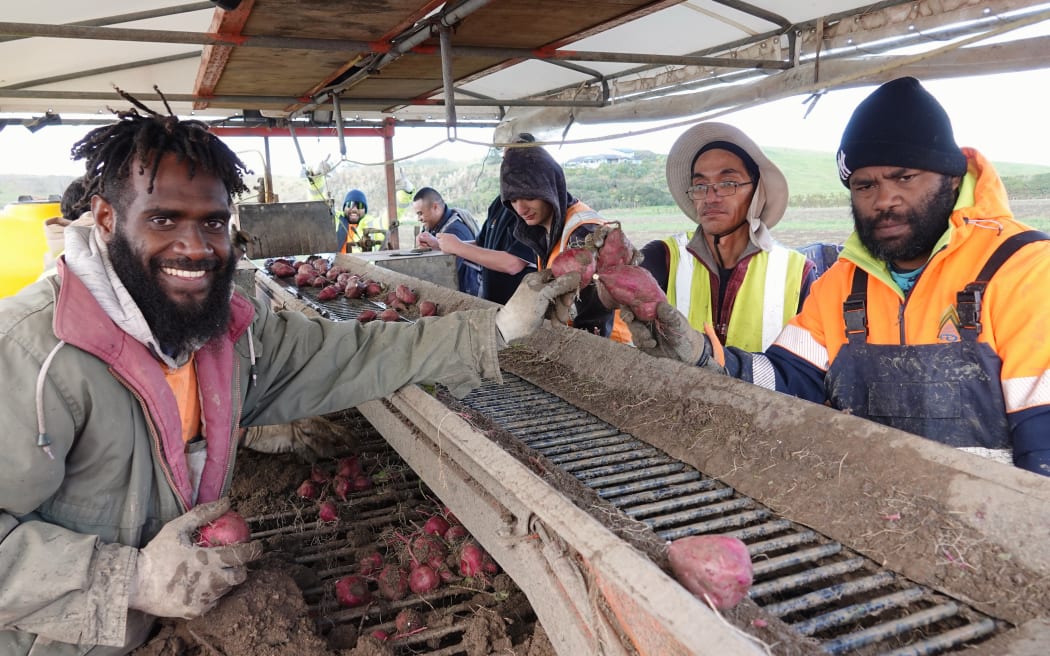

Mansen Makito, left, of Vanuatu, says the 2024 kumara crop is much better than last year’s.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
Makito was among those evacuated last year as floodwaters swamped their living quarters.
“Every part of here was flooded. It was very difficult last season but this season was really, really, really good,” he said.

Kaipara Kumara managing director Anthony Blundell checks soon-to-be-harvested kumara.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
Kaipara Kumara managing director Anthony Blundell said the “once-in-a-lifetime” 250mm of rain dumped by Cyclone Gabrielle was even more than 1988’s Cyclone Bola – and it came on the back of a wet spring and summer.
“So that 250mm of rain had nowhere to go but look for a place to make its way out to sea. It flowed over Doug’s four or five hundred acres, which included about 200 acres of kumara, so it wiped out the whole lot. It was up to the top of the fence posts. It was all just a lake.”
Overall, the district’s kumara crop dropped by 65 percent, while the volume processed at Kaipara Kumara was down 73 percent.

An estimated 95 percent of New Zealand’s kumara are grown in the Kaipara region.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
That meant the packing season finished four months early and 24 staff had to be laid off.
Some were able to work for Nilsson, who switched to courgettes so he could keep paying his staff, while others were offered part-time work at Countdown.
“But now we’re pretty much back in business as usual. It means we’ve all got work for four, five days a week, and we’ve got a lot of kumara to sell, which is great news for consumers. It couldn’t be more the opposite to 2023.”
Like Nilsson, Blundell said he was grateful to Kiwi shoppers who kept supporting growers during last year’s tough times, when kumara were scarce and prices were high.
Even with the success of the 2024 crop, Nilsson said it would take years to recover from the ravages of 2023.
“It’s going to take a fair while. Prior to this disaster last year, the year before we lost money on our crop, and the year before that was barely break-even prices.
“Financially, our resilience had ebbed away for two years. We’ve had to borrow heavily this last year to put a crop in the ground, and it’s not just going to be paid off in a year or two. Depending on the returns it could be five years, it could be 10.”
He was, however, optimistic about the future.
“I’m upbeat because I’ve got sheds full of kumara again. It’s just a question of what the price will be, if we can start paying back some debt.”

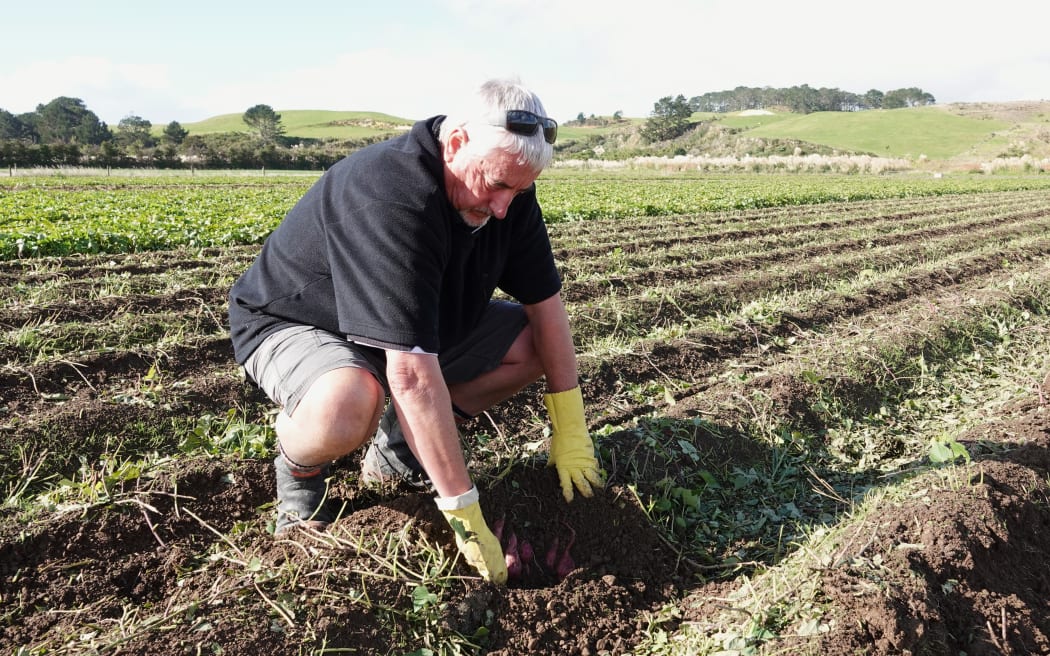
Kumara grow just below the surface of the Kaipara’s clay-rich soils.
Photo: Peter de Graaf
Nilsson said kumara and New Zealand belonged together.
“It’s a bit like the All Blacks. It’s part of New Zealand’s history, isn’t it? They’re treated as a taonga.
“It’s always been part of your diet. If you’ve got meat and veggies on your plate and there’s not a kumara amongst them, it’s not finished is it? You send the cook back to get a kumara,” he said.
The last of Nilsson’s 2024 crop was harvested on Thursday. His overseas workers are due to fly home today.